Representation of functions
A Boolean function is stored in it’s prime disjunctive normal form(which can also be interpreted as a family of sets, or a hypergraph) as a list of clauses, where the clauses are also represented as unordered lists of integer indices. For example, The Gurvich-Khachiyan exampples f_2 and g_2 are represented as:
(f-n 2) -> '((2 3) (2 4) (1 3) (1 4) (6 7) (6 8) (5 7) (5 8))
(g-n 2) -> '((3 4 5 6) (3 4 7 8) (1 2 5 6) (1 2 7 8))
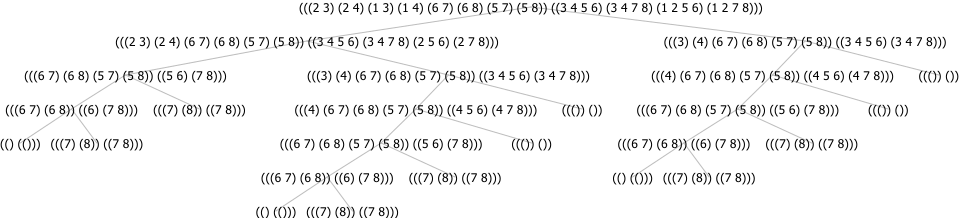
As an example of how the algorithm checks the duality of these two functions, and how this is associated with a tree, we now run through the first level of the recursion, fixing lexicographic ordering and no filtering for the pivot variables.
We split on 1 to get two subproblems:
F_1 = '((2 3)(2 4)(6 7)(6 8)(5 7)(5 8))
G_0 or G_1 = '((3 4 5 6)(3 4 7 8)(2 5 6)(2 7 8))
And
F_0 or F_1 = '((2 3)(2 4)(3)(4)(6 7)(6 8)(5 7)(5 8) = '((3)(4)(6 7)(6 8)(5 7)(5 8))
G_1 = '((3 4 5 6)(3 4 7 8))
The full recusrion tree is depicted in the following figure. The two subproblems above correspond to the left and right branches of the tree.